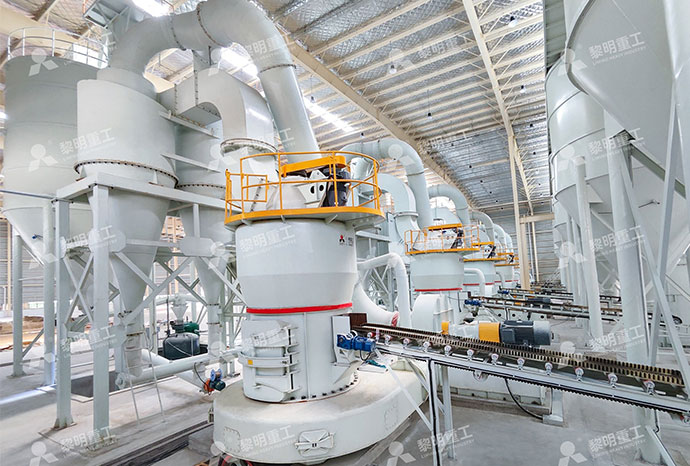
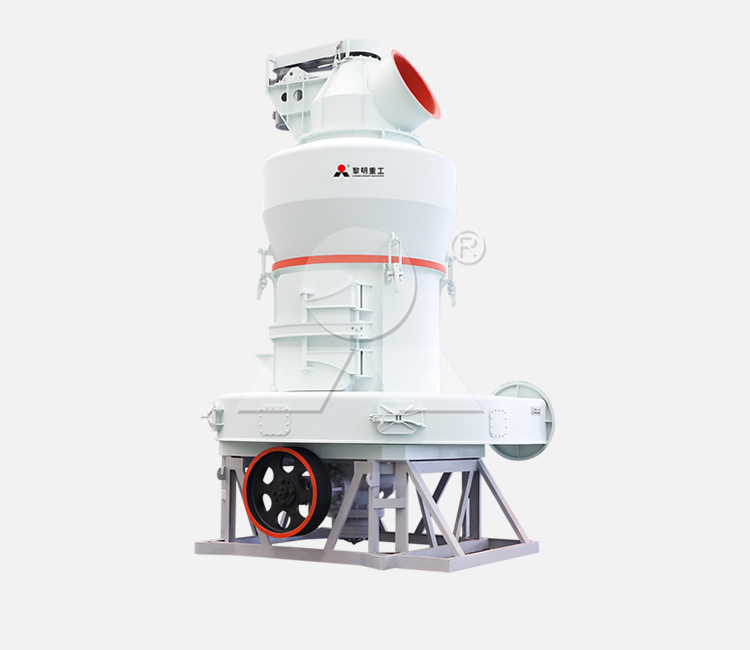
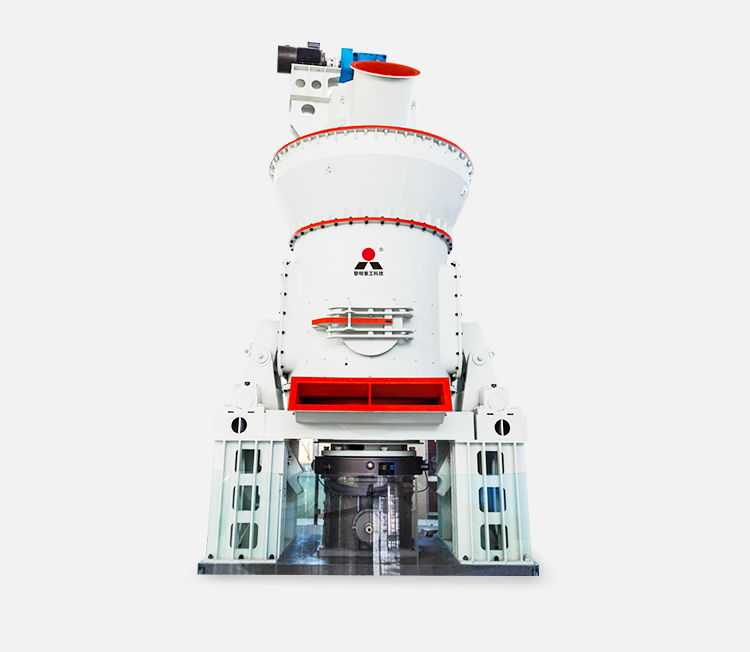
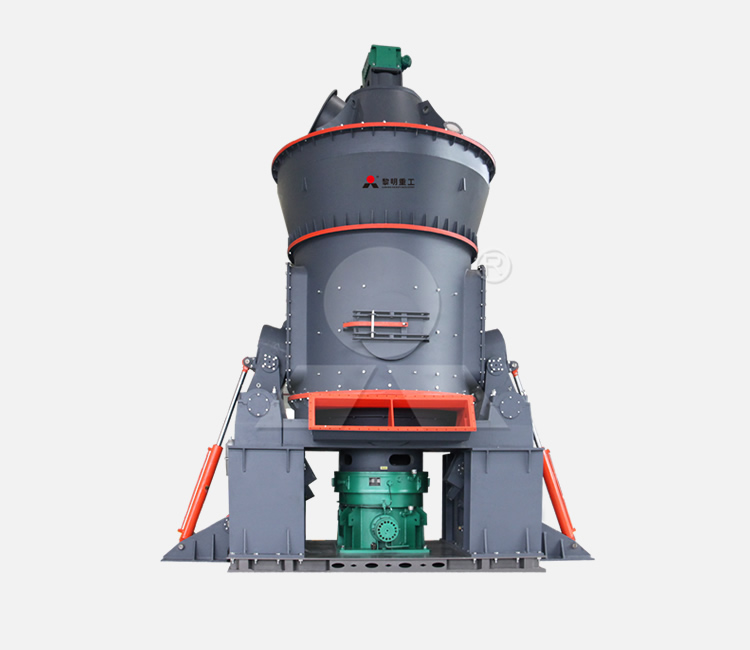
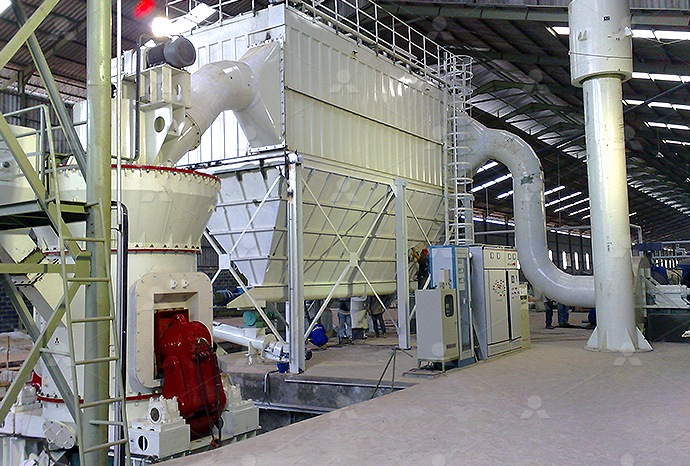
Location: Egypt
Material: Phosphate
Capacity: 70tph
Input size: <20mm
Output size: 100mesh
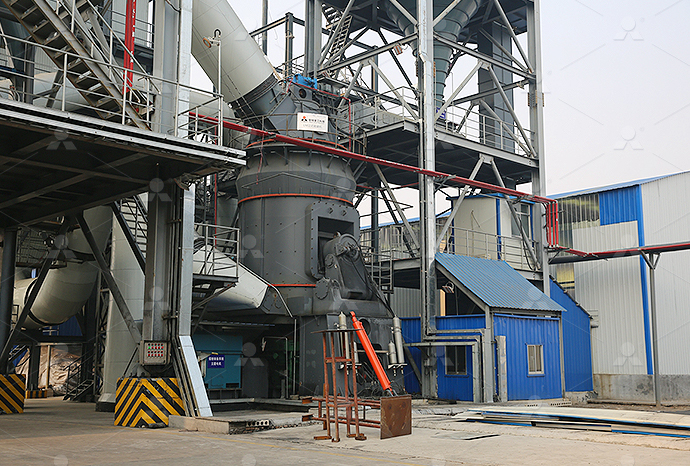
Equipment: MTW178G
Application: GSSP fertilizer
Introduction
Material Overview:Formed during the Cretaceous period (75–11 million years ago), phosphate rock consists of marine sedimentary deposits, including fragments of long bones, fish scales, teeth, and occasionally shells of foraminifera and microphosphorus debris. Natural moisture content ranges from 6% to 11%.
Applications: With a high P₂O₅ content (around 20-30%), phosphate rock serves as a key phosphorus source for the agricultural chemical industry. It is used to produce phosphate fertilizers—such as direct application ores, partially acidulated phosphate, single and triple superphosphate, phosphoric acid, monocalcium phosphate, and tricalcium phosphate for livestock feed—as well as other chemical industry products.
Processing Flow:Phosphate fertilizers are produced by chemically treating phosphate rock or powder with acids to convert the minerals into water-soluble phosphate salts. Processes include digestion with sulfuric acid, wet-process phosphoric acid production, and generating phosphoric acid and calcium sulfate. Grinding mills are used to produce 100–300 mesh phosphate powder, which is then granulated into NPK or GSSP fertilizers.